Large language models (LLMs) have drawn major public attention since the so-called ChatGPT moment in November 2022. However, within the scientific community, the so-called ImageNet moment back in 2012 — when an image recognition system based on machine learning clearly outperformed hand-crafted algorithms in a well-known benchmark — marked the beginning of an unprecedented race to develop ever more capable models. These models are now achieving human-level performance across an increasing number of disciplines and tasks. Whether it’s speech recognition, speech synthesis, text understanding, image understanding, or image generation — in all areas, the results continue to improve, often dramatically.
Audio, text, and image are considered different modalities. Since excellent results have already been achieved in each of these disciplines individually — despite some remaining shortcomings — the next step is to combine the various components into a single, unified model. The human brain serves as the inspiration for this endeavor.
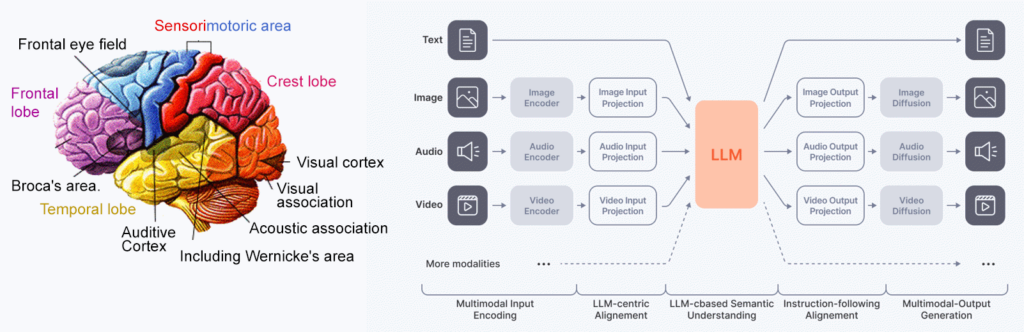
The Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Research Group is dedicated to this task, leveraging the latest foundation models from international research and adapting them for use cases in the regional economy. Smaller models for speech recognition and speech synthesis are also developed from scratch. However, in most cases, it is more energy- and cost-efficient to use pre-trained models and fine-tune them for the German language or specific company applications.
Training Data
The creation of high-quality and sufficiently large training datasets remains a central issue. The research group has built up extensive expertise in collecting and quality-assuring real-world data, as well as in generating synthetic training data. The key here lies in leveraging the best available AI models to enhance data quality and quantity — thereby enabling the training of the next generation of AI models. This results in a positive feedback loop that explains the rapid progress in deep learning over recent years.
Resource Efficiency
A key focus of our work lies in the use of resource-efficient methods — to protect the environment during both training and deployment, and to enable operation even for companies with small budgets. For training, we use parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods like Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA), and for deployment we rely on optimized runtime environments, quantized models, and well-coordinated, cost-effective hardware and software solutions.
Digital Sovereignty
The solutions we develop allow companies to decide for themselves whether they want to run AI models in their own data centers — in some cases even under their own desk — or with a German cloud provider. This way, no dependencies on multinational corporations arise. We prioritize openness, transparency, and commercial usability when selecting model
Project Experience
Through the EFRE technology transfer projects DAMMIT (Digital Transformation of SMEs through Artificial Intelligence) and M4-SKI (Multimodal Human-Machine Interface with AI), the research group has demonstrated the practical potential of its work across more than a dozen application cases. In a few instances, projects have failed despite mitigation efforts due to insufficient or overly uniform data — meaning that while models perform well on data similar to the training data, their accuracy does not always transfer to real-world use cases.
Nonetheless, it remains crucial for companies to continuously evaluate the latest technological advancements to support their business processes — to avoid falling behind as competitors achieve major savings or quality improvements through the use of AI.
Dialogue Systems
The research group focuses on assistant systems that work together with users in a dialog-driven and iterative process to achieve high-quality results. Whether using speech input and output, combining text with images, or blending text with numerical or other exceptional data types — the current capabilities to assist with work tasks that were previously fully manual are extensive. Feel free to contact us to see whether your use case could also be supported with a demonstrator.
AI Meets Virtual Reality
One particularly exciting area is the combination of multimodal AI with virtual reality as a user interface. Here, visual, speech, and text understanding come together to create new opportunities — especially in education and training — that would have seemed like science fiction just ten years ago. The research group also has years of experience in developing VR learning applications and can draw upon a rare combination of expertise that makes us an ideal research partner for many different application scenarios.
 DE
DE EN
EN